
Four devices that are active on the network. When run here, it's still missing out four devices. Oh but surely nmap is still best possible solution.But what about hackers in my network?!1.Just to play through the arguments quickly.
#Linux find mac address on network Pc
There's no direct interaction between my PC and the PVR and there aren't any services running on the PVR (no UPNP/DLNA either). To give you some sort of idea of what I mean, 10.10.0.16 above is our PVR. (To be sure you can ping all devices on the network with 10.10.0.255 first and then you will likely get 90+% of of devices.) However in my opinion modern devices are all so talkative (you should really watch wireshark - it's an education) at broadcast level that it's unlikely a device would be present on the network without at least replying to a broadcast. Otherwise, your router should be able to give you an idea of the active devices(most do).Įdit Per davidcl's comment, this answer isn't as perfect as I'd first hoped.Īrp relies on previous contact of some sort to work. If you need to parse it into something arp -an will skip the fixed width columns.

If you want it to go faster, you can use arp -n which should skip the DNS lookups. In previous releases of Nmap, -sn was known as -sP.Īrp will slowly return you a list of active MAC addresses and IPs or their hostnames if they have one. Otherwise hosts could be missed when the firewall drops probes or their responses. When strict firewalls are in place between the source host running Nmap and the target network, using those advanced techniques is recommended. If any of those probe type and port number options are used, the default probes are overridden. The -sn option can be combined with any of the discovery probe types (the -P* options, excluding -Pn) for greater flexibility. When a privileged user tries to scan targets on a local Ethernet network, ARP requests are used unless -send-ip was specified. When executed by an unprivileged user, only SYN packets are sent (using a connect call) to ports 80 and 443 on the target. The default host discovery done with -sn consists of an ICMP echo request, TCP SYN to port 443, TCP ACK to port 80, and an ICMP timestamp request by default. Often called a ping sweep, and is more reliable than pinging the broadcast address because many hosts do not reply to broadcast queries. It can easily be used to count available machines on a network or monitor server availability. Systems administrators often find this option valuable as well. Knowing how many hosts are up is more valuable to attackers than the list provided by a list scan of every single IP address and host name. It allows light reconnaissance of a target network without attracting much attention. This is by default one step more intrusive than the list scan, and can often be used for the same purposes. This is often known as a “ping scan”, but you can also request that traceroute and NSE host scripts be run. This option tells Nmap not to do a port scan after host discovery, and only print out the available hosts that responded to the scan. Here is a little quote from the man page, nmap(1): -sn (No port scan)

Network ID is 192.168.3.0, just substitute the last number by 0.

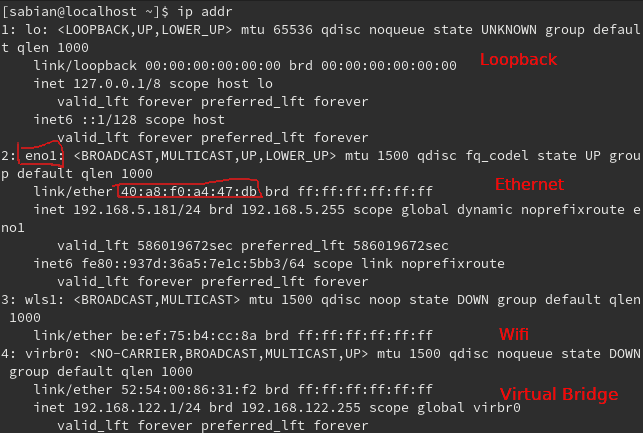
Here at point 2, I have the wlan0 device. Inet6 fe80::c685:8ff:fe94:ee9a/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever Inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverĢ: wlan0: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000 Please substitute your network identifier and subnet mask.ġ: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
